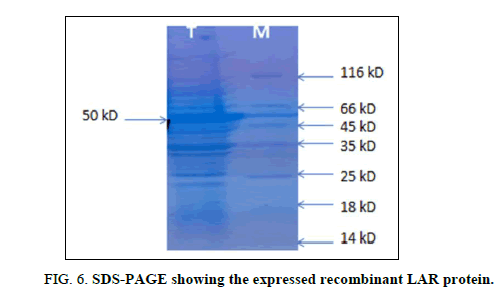
In enzymology, a leucoanthocyanidin reductase (EC 1.17.1.3) (LAR, aka leucocyanidin reductase or LCR) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- (2R,3S)-catechin NADP H2O 2,3-trans-3,4-cis-leucocyanidin NADPH H
The 3 substrates of this enzyme are (2R,3S)-catechin, NADP , and H2O, whereas its 3 products are 2,3-trans-3,4-cis-leucocyanidin, NADPH, and H .
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on CH or CH2 groups with NAD or NADP as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is (2R,3S)-catechin:NADP 4-oxidoreductase. This enzyme is also called leucocyanidin reductase. This enzyme participates in flavonoid biosynthesis.
The enzyme can be found in the plant Hedysarum sulphurescens and in Vitis vinifera (grape).
References
Further reading